- India
- International
UPSC Key | 30th April, 2024 — International Criminal Court, MCC, Critical minerals and more
Exclusive for Subscribers from Monday to Friday: How are International Criminal Court (ICC) and Model Code of Conduct (MCC) relevant to the UPSC Exam? What significance do topics like Ethylene Oxide and Critical Minerals have for the preliminary and main exams? You can learn more by reading the Indian Express UPSC Key for April 30, 2024.
 Israel is voicing concern that the International Criminal Court could be preparing to issue arrest warrants for government officials on charges related to the conduct of its war against Hamas.
Know more in our UPSC Key.
Israel is voicing concern that the International Criminal Court could be preparing to issue arrest warrants for government officials on charges related to the conduct of its war against Hamas.
Know more in our UPSC Key.Important topics and their relevance in UPSC CSE exam for April 30, 2024. If you missed the April 29, 2024 UPSC CSE exam key from the Indian Express, read it here.
🚨 The Indian Express UPSC Essentials brings to you the April edition of its monthly magazine. Click Here to read. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
The World
Potential ICC arrest warrants elicit concern among Israel’s top officials
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: GS-II: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
What’s the ongoing story- Israel is voicing concern that the International Criminal Court could be preparing to issue arrest warrants for government officials on charges related to the conduct of its war against Hamas.
Prerequisites:
— What is the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
— What is International Court of Justice?

— International Criminal Court and International Court of Justice-Compare and Contrast
Key takeaways:
— The ICC – which can charge individuals with war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide – is investigating Hamas’ October 7 cross-border attack and Israel’s devastating military assault on Hamas-ruled Gaza.
— Israeli officials are worried that the court could issue arrest warrants against Netanyahu and other top officials for alleged violations of international humanitarian law in Gaza, Israeli media have reported.
— Israel is not a member of the court and does not recognise its jurisdiction, but the Palestinian territories were admitted with the status of a member state in 2015.
— The ICJ, also known as the World Court, is a United Nations court that deals with disputes between states, while the ICC is a treaty-based criminal court focusing on individual criminal responsibility for war crimes.
For Your Information:
— The 1949 Geneva Conventions are a set of international treaties that ensure that warring parties conduct themselves in a humane way with non-combatants such as civilians and medical personnel, as well as with combatants no longer actively engaged in fighting, such as prisoners of war, and wounded or sick soldiers.
— All countries are signatories to the Geneva Conventions.
Points to Ponder:
— Why is India not a member of the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
— What are the emerging challenges in the field of international criminal justice?
— What are war crimes? What is the criteria for war crimes?
— What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
— What are the provisions related to human rights in India?
— What distinguishes war crimes from crimes against humanity?
Post Read Question:
Which of the following statements is not correct with reference to the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
(a) Governed by an international treaty called ‘The Rome Statute’, the ICC is the world’s first permanent international criminal court.
(b) It investigates and, where warranted, tries individuals charged with the gravest crimes of concern to the international community: genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity and the crime of aggression.
(c) India is not a party to Rome Statute along with US and Britain.
(d) ICC headquarters at The Hague, the Netherlands.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Everyday Global: What is the International Court of Justice
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
The Editorial Page
Mind the gap
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues
Mains Examination: GS-II, Constitution, Polity
What’s the ongoing story- Former Election Commissioner Ashok Lavasa writes: a significant gap in the present framework is that the Model Code of Conduct for elections has not clearly spelt out the consequences of defaults, thus diluting its deterrent effect.
Prerequisites:
— What is the role of the Election Commission of India?
— What is the Model Code of Conduct (MCC)?
— What is vicarious liability?
Key takeaways:
— Ashok Lavasa opines, “There is a need to remodel MCC by imposing more reasonable restrictions in a non-discriminatory manner.”
—” A significant gap in the present framework is that the MCC has not clearly spelt out the consequences of defaults, thus diluting its deterrent effect. It is necessary to specify punitive measures in a fair, transparent, and predictable manner, especially with respect to serious violations.”
— “Such violations should attract severe consequences that could be graded and made known publicly.”
— He has provided examples of how MCC can be revamped. “the first case of any such violations could attract a ban on campaigning for a specified period; the second could entail a ban for a longer period and the third would debar the concerned candidate or political functionary for the entire period while the MCC is in force.”
— “ Those found in repeated violation would not be eligible to be categorised as star campaigners in subsequent elections for a certain length of time.”
— “In an unprecedented move when the EC served a notice to political parties for violation alleged to be committed by individuals has introduced the principle of vicarious liability.”
— “The procedure for dealing with such cases should be streamlined such that punitive action is taken within 72 hours of the violation. A standard procedure must be laid down. Delayed responses dilute the impact of penalties and diminish public confidence in the credibility of the EC.”
— “Whether all this will deter potential violators and instil an element of self-regulation in the conduct of political parties, depends on the character of the political leaders.”
For Your Information:
— Kerala was the first state to adopt a code of conduct for elections. In 1960, ahead of the Assembly elections in the state, the administration prepared a draft code that covered important aspects of electioneering such as processions, political rallies, and speeches.
— It was only in 1974, just before the mid-term general elections, that the EC released a formal MCC. It also set up bureaucratic bodies at the district level to oversee its implementation.
— So the EC, just before the 1979 Lok Sabha elections, released a revised Model Code with seven parts, with one part devoted to the party in power and what it could and could not do once elections were announced. The MCC has subsequently evolved as an integral part of conducting fair and free elections.
Points to Ponder:
— When did MCC come into force?
— What is the statutory status of MCC?
— Criticism related to MCC
— Recommendation of various committees on the implementation of MCC
— Role of Election Commission in the implementation of MCC
(Thought process: Goswami Committee on Electoral Reforms, recommendation of law commission, significance of Chief Election Officer in strict implementation of MCC like T.N. Seshan)
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Which was the first state to implement the Model Code of Conduct (MCC)?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Kerala
(c) Karnataka
(d) Andhra Pradesh
Mains
Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Decode Politics: Key to free and fair polls, how Model Code of Conduct evolved over decades
Model Code of Conduct comes into force for 2024 Lok Sabha elections: What does it mean?
Short on safety
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national importance.
Mains Examination: GS-II: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
What’s the ongoing story- In the past few weeks, questions have been raised about India’s food safety regime in the wake of allegations against products as varied as infant food, “health drinks” and spices.
Prerequisites:
— What is FSSAI? What are the legislative frameworks of FSSAI?
— What is Salmonella?
— What is ethylene oxide?
Key takeaways:
— Frequent controversies over food products in India show the country’s food business regulator in poor light and FSSAI needs to step up.
— The FSSAI came into being in 2008, two years after the enactment of the Food Safety and Standards Act. Its remit extends to multinationals like Nestle and Cadbury, established Indian companies like MDH and Everest and thousands of small and medium-sized food businesses who have razor-thin profit margins.
— The agency has had a chequered record. It has consistently been hamstrung by staff and infrastructure shortage. This has meant that a large section of the market views regulation as paperwork rather than regular inspections followed by expert guidance.
— The FSSAI is mandated to educate businesses and consumers on food safety. It is also tasked to “collect and collate data regarding food consumption, incidence and prevalence of biological risk, contaminants in food, residues of various contaminants in foods products, and identify risks”. The frequent controversies around food items indicate that the agency has done scarce justice to its remit.
— Regulations must contend with scientific uncertainty and the variance in rules amongst nations. Thus, food authority must regularly update standards, and handhold exporters. The FSSAI has fallen short on both counts. The failure of MDH’s plants to meet the USFDA sanitary standards shows the Indian regulator in poor light. A country with a growing food market and an aspiration to increase its footprint in the global market needs a more proactive regulator.
For Your Information:
— Salmonella is a group of bacteria that can cause food-borne illnesses known as salmonellosis. The World Health Organisation (WHO) identifies Salmonella as one of four key global causes of diarrhoeal diseases. Individuals who develop salmonellosis may show symptoms such as nausea, diarrhoea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12-72 hours after contracting the infection.
Points to Ponder:
— Why is food safety an important issue? What are WHO’s five keys to safer food?
— What are the challenges associated with the food safety in India?
— What are some of the important initiatives for food safety in India?
— What is the State Food Safety Index (SFSI)?
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Consider the following statements about the State Food Safety Index (SFSI):
1. The index is released by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to measure the performance of States/UTs on various parameters of Food Safety.
2. The index is released bi-annually.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? given below –
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Mains
What should be the role of different stakeholders in food safety?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
FSSAI sets up lab network to test food for pathogens
Explained: MDH masalas in US have tested positive for Salmonella. What is it?
The Ideas Page
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity- Constitution, Right Issues, Social Sector Initiatives.
Mains Examination: GS-I: Society, Issues related to women, Social empowerment.
What’s the ongoing story- Ashwini Deshpande writes- “Which parent is primarily responsible for the hands-on work that goes into raising children until they are adults? In India, like elsewhere in the world, it is typically the mother. The central government has a childcare leave (CCL) policy which allows for 730 days of paid leave to female employees during their entire service period, for taking care of a maximum of two children under 18 years. This is over and above maternity leave.”
Prerequisites:
— What are the key provisions of the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, and the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017?
— What is the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013?
— What are the articles of the Indian Constitution related to gender equality and women?
(Thought Process: Read articles 14, 15, 16, 21, 39, 39(A), 42, 51 A (e), Reservation of Seats for Women in Panchayats and Municipalities.)
— What is the provision with regard to childcare leave in India?
Key takeaways:
— Child Care Leave (CCL) is a central government provision that is not binding on the states. Recently, a government employee in Himachal Pradesh was denied the CCL. The Supreme Court declared this denial as a violation of working women’s “constitutional right”.
— Provisions of the Maternity Benefit Act, or the POSH (Prevention of Sexual Harassment) Act are applicable to establishments with 10 or more employees. Majority of firms in India are not covered by any of these benefits because they are too small. The Economic Census reveals that 98 per cent firms are “micro”, i.e., they have less than 10 employees.
— The ground reality is that the pro-women laws, which are meant to ensure constitutional rights, are applicable to a small minority of employed women. In the larger establishments (i.e., private establishments with more than 10 workers) where POSH and maternity laws are applicable, research hints at perverse consequences, such that in the short run, these have the potential to worsen employer bias against women.
— This doesn’t mean that there should not be pro-women laws, even if applicable to a tiny proportion of workers. Wherever possible, legal structure needs to guarantee women’s rights.
— However, we also need to think more broadly about how to effectively ameliorate the burden of childcare that is seen as essentially the mothers’ responsibility. The 3Rs framework shows the way forward: Recognise, reduce, and redistribute the responsibility of childcare. Through redistribution, both within the household and outside.
— Both in urban and rural areas, we need good quality, affordable, reliable and safe childcare in our neighbourhoods. This can be provided both by government and private players. We also need to invest in the care economy.
For Your Information:
— Men are eligible for CCL only if they are single fathers.
Points to Ponder:
— How pro-women laws have the potential to worsen employer bias against women.
— What is the care economy?
— What are the government’s initiatives for promoting women’s empowerment?
— What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space?
Post Read Question:
Distinguish between ‘care economy’ and ‘monetized economy’. How can care economy be brought into monetized economy through women empowerment? (2023)
“Today’s children are tomorrow’s workforce and therefore childcare is a social responsibility.” In the light of this statement, elaborate what measures should be taken to effectively ameliorate the burden of childcare that is seen as essentially the mothers’ responsibility.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
SC: Denying women child care leave is violation of Constitution
Explained
Repolls and adjournments: ECI’s options when polling process is disrupted
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues
Mains Examination: GS-II, Constitution, Polity
What’s the ongoing story- The Election Commission of India (EC), under Sections 58(2) and 58A(2) of the Representation of People Act, 1951 (RPA), declared void the poll on April 19, in 11 polling stations of Manipur, and 8 polling stations of Arunachal Pradesh. Repolls were conducted on April 22 and April 24 respectively. Elections were also adjourned in Madhya Pradesh’s Betul Lok Sabha constituency due to the death of a candidate on April 9. The polling, originally scheduled on April 26, will now be held on May 7.
Prerequisites:
— Who is the Returning Officer (RO)?
— Who is the Presiding Officer (PO)?
— Who is the Chief Electoral Officer (CEO)?
— What is the Representation of the People Act, 1951 (RPA)?
— Role of the Election Commission of India (ECI)
Key takeaways:
— Ravi Mittal writes: “India’s election laws provide a framework for handling situations where the normal polling process is disrupted for any reason, including damage to EVMs, booth-capturing, natural disasters, or a candidate’s death.”
— “Under Section 58 of the RPA (‘Fresh poll in the case of destruction, etc., of ballot boxes’), the EC can declare the poll at a polling station to be void if unauthroised person has taken away EVM, EVM accidentally or intentionally destroyed, and a mechanical failure develops in any EVM during the recording of votes.”
— “Section 135A of the RPA defines booth booth capture. Booth capturing is punishable for a term of not less than one year, which may extend to three years for lay people, and not less than three years, extending to five years for government servants.”
— “The Presiding Officer of a polling station can adjourn the poll at a polling station under section 57(1) of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, in case of: natural calamity, . interruption or obstruction due to any riot or, open violence, non-arrival of the polling party due to obstruction or any other serious difficulty.”
— “As per Section 52 of RPA, amended in 1996, the poll shall be adjourned only in case of the death of a recognised political party’s candidate. The above provision applies if the candidate with a valid nomination dies at any time after 11.00 a.m. on the last date for making nominations, until the commencement of the poll.”
For Your Information:
— “The ECI’s vital function is to ensure free and fair elections leading to the formation of a democratically-elected political system responsible for running the government till the next elections.”
— In Betul, the candidate’s death occurred one day after the last day for withdrawing candidature. Therefore, the polls were adjourned. However, in the Moradabad Lok Sabha constituency, the candidate died after voting, in which case a by-election will be held if he emerges as the winner of the seat after counting.
Points to Ponder:
— Role of ECI in conducting free and fair elections
— What measures have been taken by the ECI to eliminate booth capture?
— Coordination and Cooperation between RO, PO, CEO and ECI.
Post Read Question:
Consider the following statements:
1. Section 58 of the RPA, 1951 provides power to the ECI to declare the poll void in case any mechanical failure develops in any EVM during the recording of votes.
2. Section 52 of the RPA allows the ECI to adjourn the polling if the candidate contesting the election from a “recognised political party” died after voting.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d)Neither 1 nor 2
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Hangor class submarine
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: GS-III: Security, Defence Technology.
What’s the ongoing story- The first Hangor class submarine, built by China for Pakistan, was launched on April 26 at a Wuhan shipyard. This was the first of eight submarines of this class that the Pakistan Navy is set to induct into its fleet by 2028. Here is all you need to know.
Prerequisites:
— What are diesel-electric submarines?
— What are the major types of submarines?
— Read about India’s Kalavari class of submarines.
Key takeaways:
— The Hangor-class, an export variant of the Chinese Type 039A Yuan class, is a diesel-electric attack submarine, named after the now decommissioned PNS Hangor, which famously sank Indian frigate INS Khukri during the 1971 war.
— “Diesel-electric” refers to the mode of propulsion — diesel engines power the submarine when surfaced or snorkelling (as they need air to operate), while a battery, charged by the diesel engine, allows the vessel to operate while submerged.
— Pakistan’s Hangor class is the direct counterpart of India’s Kalavari class of submarines, based on the French Scorpene-class. India currently operates six Kalavari class submarines, with three more set to be inducted into service by the early 2030s.
— In terms of size, the Hangor class is significantly bigger than the Kalavari class. The Kalavari class, like the Hangor class, runs on diesel-electric propulsion. However, the models India currently operates do not come with built-in AIP. This means that in terms of underwater endurance, the Hangor class potentially has an edge on the Kalavari class.Both submarine classes carry state of the art sensor suites, although details of Hangor’s capabilities in this regard are not out in public.
For Your Information:
— India got its first submarine, INS Kalvari of the Foxtrot Class, from the USSR in December 1967.
Points to Ponder:
— What is the significance of submarines to India?
— What are the issues with the submarine capability of India?
— How many submarines does India have? What is Project-75?
— How many submarines do China and Pakistan’s navies possess in their fleets?
— What is China’s maritime defense capability, and why is it a concern for India?
Post Read Question:
Which of the followings are submarines?
1. Kalvari
2. Vagir
3. Vagsheer
4. Vela
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Explained: The state of India’s submarine fleet
Economy
20 critical mineral blocks to be on sale
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian and World Geography – Physical, Social, Economic geography of India and the World.
Mains Examination: GS-I, GS-II, GS-III: Distribution of key natural resources across the world, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests, Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life, Defence.
What’s the ongoing story- The government will put on sale around 20 critical mineral blocks in the fourth round of auction by the end of June, mines secretary V L Kantha Rao said on Monday.
Prerequisites:
— What is an auction?
— What are critical minerals?
Key takeaways:
— Critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt and rare earth elements are essential components in many of today’s rapidly growing clean energy technologies –- from wind turbines and electricity networks to electric vehicles.
— Demand for these minerals is growing quickly with clean energy transitions gathering pace.
For Your Information:
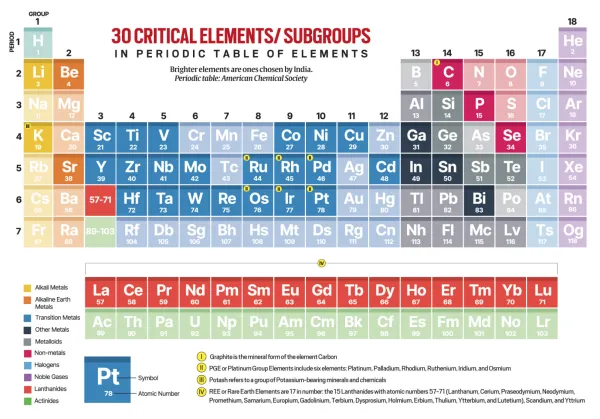
— Minister Joshi told Lok Sabha in August 2023 that in FY23, India imported 2,145 tonnes of lithium carbonate and lithium oxide at a total cost of Rs 732 crore.
— India also imported 32,000 tonnes of unwrought nickel at a cost of Rs 6,549 crore, and 1.2 million tonnes of copper ore at a cost of Rs 27,374 crore, in 2022-23.
— India is 100 per cent reliant on imports for its lithium and nickel demand. For copper, this figure is 93 per cent.
— India has identified 30 critical minerals in July 2023 depending upon their disruption potential, substitutability, cross-cutting usage across different sectors, import reliance, recycling rates etc.
Points to Ponder:
— India has collaborated with which countries on critical minerals?
— How critical minerals hold a vehicle for India’s development?
— Role of private sectors in exploring critical minerals.
— What is the significance of critical minerals in clean technology initiatives, semi-conductors, and advanced manufacturing inputs?
— What are the challenges India faces in assuring resilient critical minerals supply chains?
— Role of US-led Minerals Security Partnership (MSP)? Is India part of this partnership?
Post Read Question:
Discuss the significance of critical minerals in multiple strategic value chains. What steps have been taken by the Indian government in the exploration of the critical minerals?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Mining for critical minerals: what is the auction process, and why is it important?
Centre identifies 30 critical minerals: Why, how, and importance of the exercise
Govt & Politics
India summons Canada diplomat over pro-Khalistan slogans in Toronto
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II: International Relations
What’s the ongoing story– India on monday summoned the Canadian Deputy High Commissioner and lodged a strong protest over the pro-Khalistan slogans raised during a public event in Toronto in the presence of Prime Minister Justin Trudeau.
Prerequisites:
— What is the Khalistan Movement?
— What is the separatist movement?
Map Work: Location of Canada on the world map.
(Great Lakes: Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario are located in Canada)
Key takeaways:
— “At the event on Sunday, as the Canadian PM walked up to the stage for his address to mark Khalsa Day, the chants of “Khalistan Zindabad” kept getting louder, showed a video released by Canadian TV channels.”
— It happened again when Opposition leader Pierre Poilievre walked up to the stage to begin his address. New Democratic Party leader Jagmeet Singh and Toronto Mayor Olivia Chow were also present at the event.
— “Trudeau, who has upset India with allegations that Delhi was involved in the killing of Sikh separatist Hardeep Singh Nijjar last year, also vowed to always protect the rights and freedoms of Sikhs in Canada.”
For Your Information:
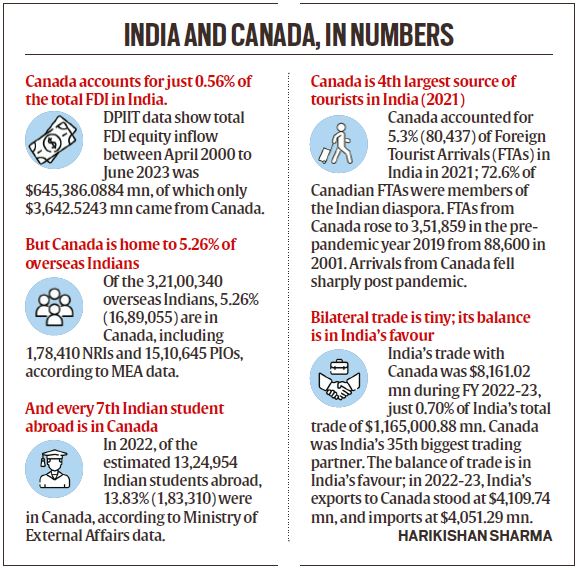 Source: The India-Canada standoff: What led to it, the problems it raises (The Indian Express, September 22, 2023)
Source: The India-Canada standoff: What led to it, the problems it raises (The Indian Express, September 22, 2023)
— In September last year, India suspended visa services to Canada which was restored after some time. India has also revoked the diplomatic immunity of Canadian diplomats based in India.
— The big issue for India is the safe haven that Canada has provided to separatist Khalistani groups, and what New Delhi sees as the Liberal Party’s pandering to these groups for votes. Estimates suggest there are 20-25 constituencies where these votes are crucial — and that explains the Trudeau government’s soft-pedalling on India’s concerns.
— In geopolitics: Canada is an important strategic partner for major Western powers — it is part of the G7 grouping and shares the table with the US, UK, Germany, France, Italy, and Japan. It also shares intelligence with the Five Eyes grouping — with the US, UK, Australia, and New Zealand.
Points to Ponder:
— What are the reasons for the rise in pro-khalistani activities?
— What is the impact of diplomatic escalation on India and Canada trade ties?
— Impact of the turmoil of relationship on the Indian diaspora in Canada
Post Read Question:
How is the Khalistan Issue impacting the bilateral relationship between India and Canada? What potential steps need to be taken to restore the values of trust and loyalty between these two nations?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
A history of the Khalistan movement in Canada, going back more than 40 years
The India-Canada standoff: What led to it, the problems it raises
UPSC Ethics and Essay Snippet
‘Wordly Wise’ from The Editorial Page
“We are stuck with technology when what we really want is just stuff that works.”
-Douglas Adams
(Thought process: While technology is often seen as the answer to our problems or the key to a better life, what people truly desire are simple tools or solutions that effectively serve their purpose without unnecessary complexity. In contrast to it, do you think, emerging technologies are presenting new challenges to society and are opening new fronts of complexity in the form of the misuse of AI and other technologies? How can we draw the line between the optimal yet right use of technology and its misuse? Is the cost of a simple life through advanced technology higher than ever before? Is it the fallacy in the technology or in its way of use that is increasing the complexities of human life rather than making it simple? Also, refer Express View.)
“You cannot have a proud and chivalrous spirit if your conduct is mean and paltry; for whatever a man’s actions are, such must be his spirit.”
–Demosthenes
(Thought process: Emphasis on aligning one’s action with values and character. Social status or external appearance doesn’t determine the nobility and honour of a person. Isn’t the conduct of a person the most important thing? Let’s refer to an example for our Ethics and Essay papers: The Seshan effect -“The story of T.N Seshan (Chief Election Commissioner) and the EC is a striking example of the transformation an individual can achieve in a complex society with multiple levers of power. In retrospect, all that Seshan did was enforce the EC’s authority as per its powers laid out in the Constitution. When the pushback came from the politicians, he stood his ground with the backing of the law. In clashes with the political class, his persona, aggressive, even abrasive, loomed larger than life, but it was the institution that ultimately won the battle.” What other examples can you think of from the lives of different personalities justifying this quote? For more refer to ‘Mind the gap’.)
May 16: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05